Fiber
-
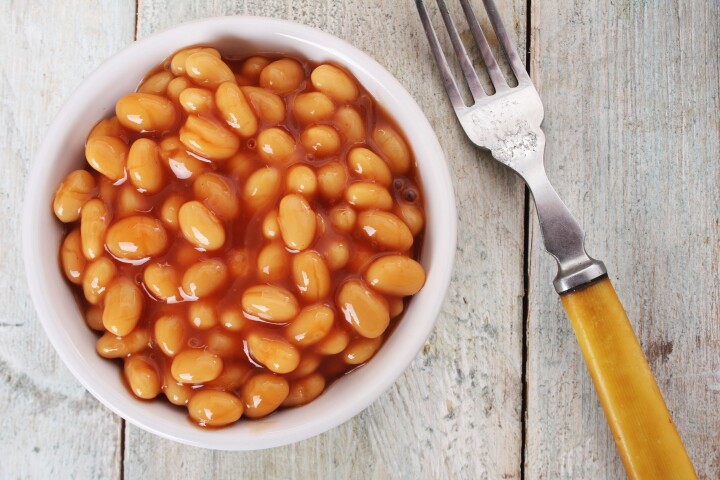
Beans don't have the best rep when it comes to our guts. But a new study has shown how a daily dose of navy beans can easily restore gut health in colorectal cancer survivors, revealing their broad benefit in helping protect against chronic diseases.
-
Up to four million Americans may be enduring this common ailment right now. But what if a microbe found in the gut could relieve it and restore gut health? Scientists believe they've found the genetic key that powers this microbe's motility engines.
-
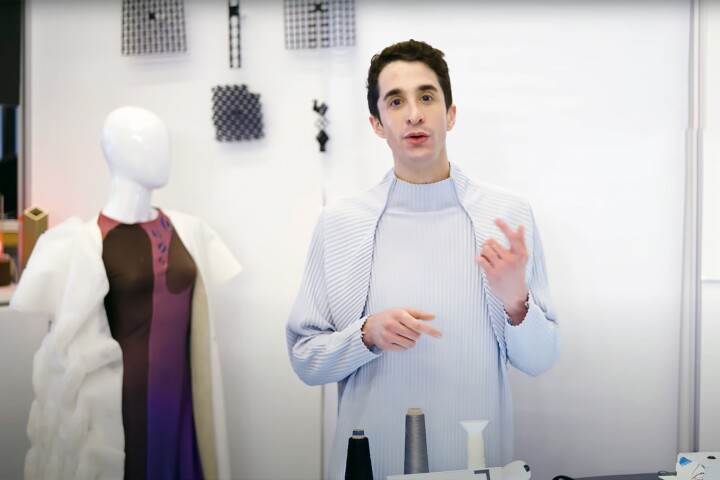
Researchers have created a low-cost fiber that contracts in response to heat, resuming its shape when the heat is removed. Compatible with existing textile-producing machinery, the shape-shifting fiber could have a myriad of uses.
-
Researchers have demonstrated a form of fermentable fiber can lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. The placebo-controlled trial revealed just three weeks of supplementation decreased blood pressure as effectively as currently used drugs.
-
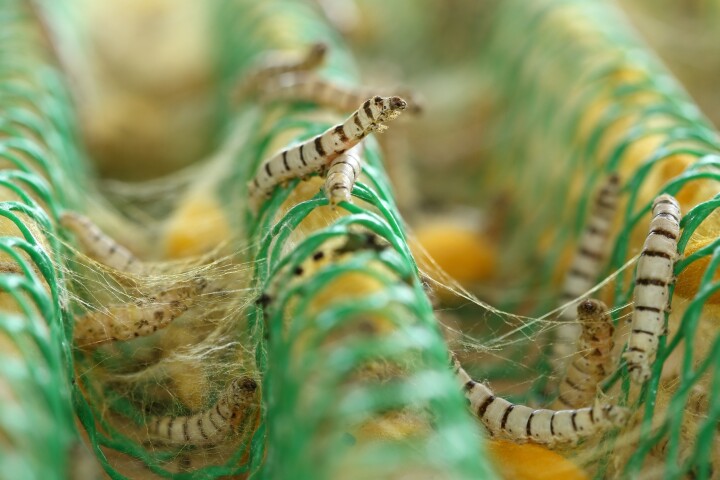
Nanofibers have recently been utilized in many applications, ranging from wound dressings to high-strength composite materials. Scientists have now developed a faster and simpler method of producing those fibers, which was inspired by the silkworm.
-
RMIT researchers claim FiberX can add up to 20% more healthy dietary fiber to food, without any detectable change to its color, texture or taste. Best of all, the team says it can be made from starches that would otherwise be agricultural waste.
-
Researchers in Germany have demonstrated quantum entanglement of two atoms separated by 33 km (20.5 miles) of fiber optics. This is a record distance for this kind of communication and marks a breakthrough towards a fast and secure quantum internet.
-
Smart textiles are usually fairly limited in size and scope. Now a team of scientists has woven together a 46-inch textile display, loaded with LEDs, sensors and energy storage, which can be made using existing industrial manufacturing processes.
-
"Muscle shirt" may soon take on a whole new meaning. A team has found a way to use bacteria to produce synthetic muscle proteins, which can then be spun into fibers to make clothing, protective gear and biomedical implants and prosthetics.
-
A trial testing fecal transplants in obese subjects with metabolic syndrome found the treatment was only beneficial when accompanied by non-fermentable fiber supplements. The trial saw improvements in insulin sensitivity 6 weeks after a fecal transplant.
-
Tiny robots could serve useful functions, but shrinking actuators has proven challenging. Now researchers at the University of Wollongong have made artificial muscles that surpass your puny natural ones, inspired by the “supercoiling” of DNA strands.
-
The brewing of beer produces great quantities of leftover grain, which often ends up being processed into cattle feed. Scientists have developed a new method of extracting the protein and fiber from that waste, however, for use by humans.
Load More